Team Teach Group 1
Undecidable Problems
- Undecidable and Decidable Problems in Computer Science
- Example inputs and outputs
- College Board MC examples:
Undecidable and Decidable Problems in Computer Science
Undecidable Problems
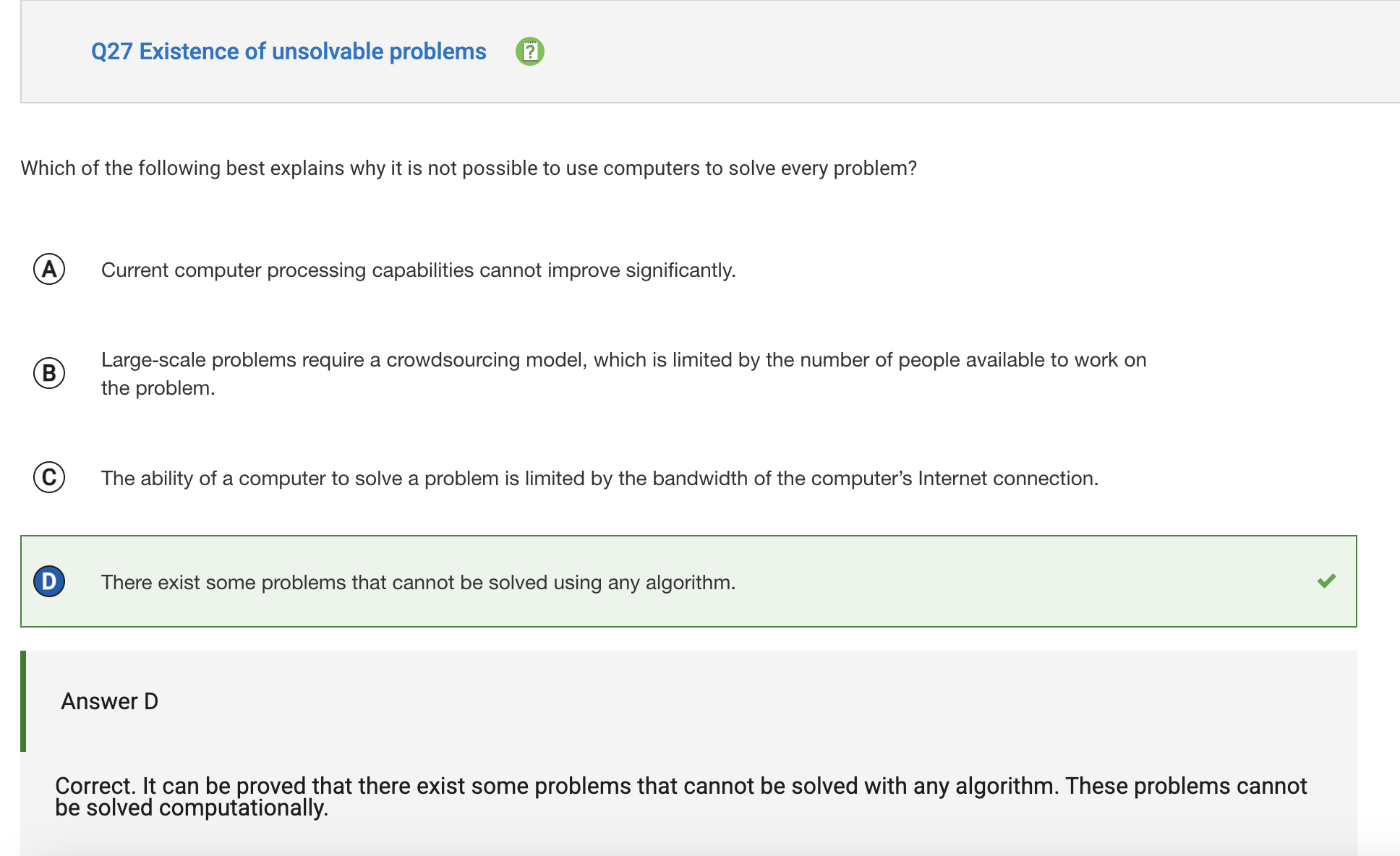
An undecidable problem is a problem for which no algorithm can be constructed that will always provide a correct yes/no answer for all possible inputs.
Key Characteristics:
- No single algorithm can always provide a correct answer.
- Some instances may have a solution, but no algorithm can solve all instances.
- A classic example is the Halting Problem.
Example: The Halting Problem
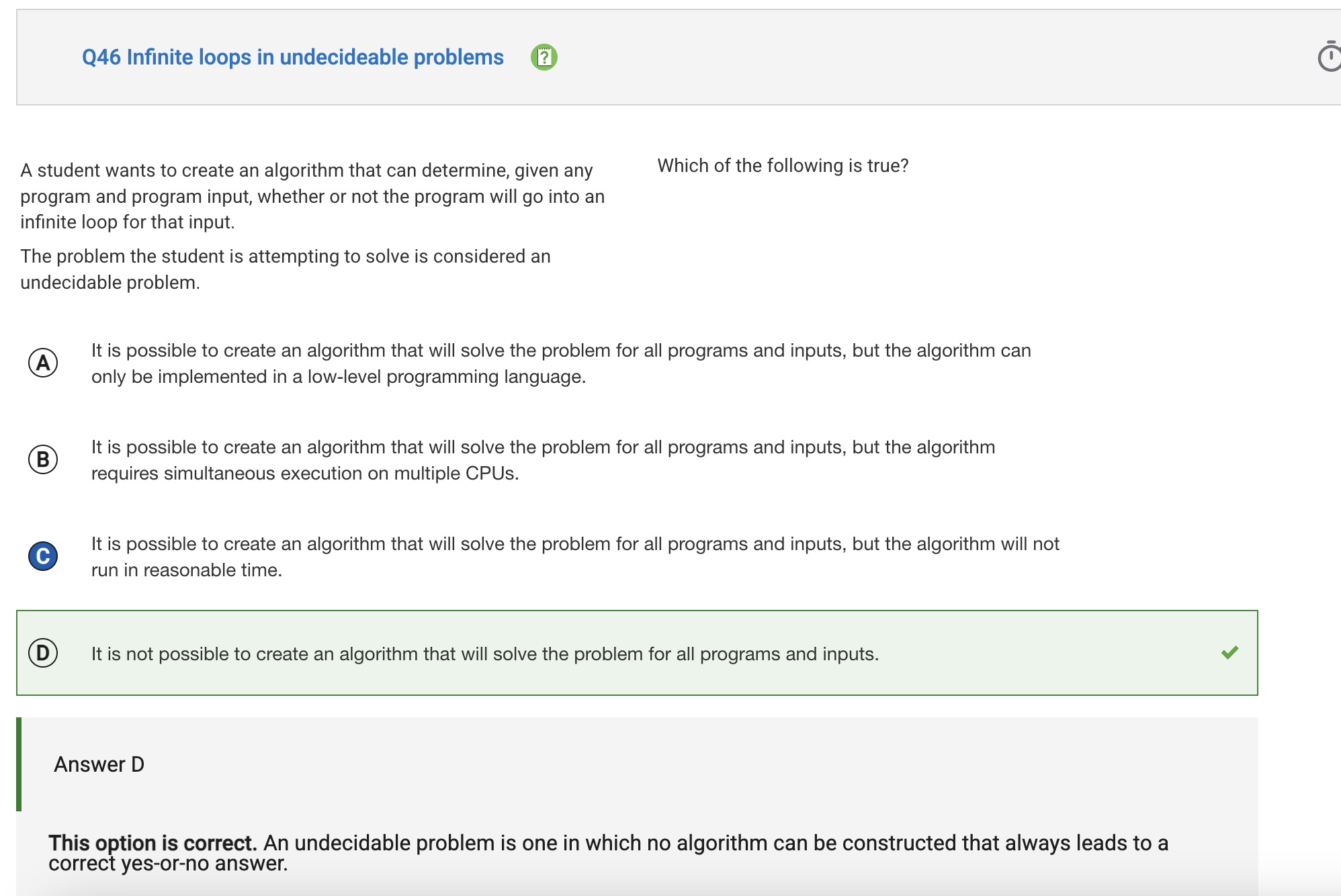
Alan Turing introduced the Halting Problem, which asks whether a given computer program will eventually stop (halt) or continue running forever when given a specific input.
- Alan Turing proved that it is impossible to create an algorithm that can determine whether every possible program will halt or run forever.
- Sometimes a program might take an unreasonable amount of time to reach an ending—if it even exists.
Real-World Analogy: A Website Taking Too Long to Load
Imagine you click on a website, and it just keeps loading indefinitely.
- Is the page taking a long time to load, or will it never load?
- There is no general way to determine if the website will ever finish loading.
- Just like the Halting Problem, we cannot predict for all cases whether a webpage will load successfully.
Decidable Problems
A decidable problem is a problem for which an algorithm can always be written to provide a correct yes/no output for any input.
Key Characteristics:
- An algorithm exists that solves every possible case of the problem.
- The algorithm always terminates with a correct answer.
- Example: Checking if a number is divisible by 3.
Example: Checking Divisibility by 3
Below is a Python program that checks whether a number is divisible by 3:
def is_divisible_by_3(n):
return n % 3 == 0
Example inputs and outputs
print(is_divisible_by_3(9)) # Output: True
print(is_divisible_by_3(10)) # Output: False
print(is_divisible_by_3(21)) # Output: True
Popcorn Hack 1
An algorithm can be used to solve an undecidable problem. (True/False)
Popcorn Hack 2
If a programmer encounters an undecidable problem, they can just use an alogirhtm that works most of the time. (True/False)
Popcorn Hack 3
Which of the following options is not an example of an undecidable problem?
A. Halting Problem
B. The Collatz Conjecture
C. Rice’s Theorem
D. Bubble sorting
ANSWER: D
College Board MC examples:
Undecideable Problems Homework:
Question/research:
Investigate and describe how modern operating systems and browsers handle infinite loops or excessively long-running scripts. What mechanisms are in place to detect and mitigate such issues? Provide real-world examples of these mechanisms in action, such as specific error messages, timeouts, or automated recovery processes.